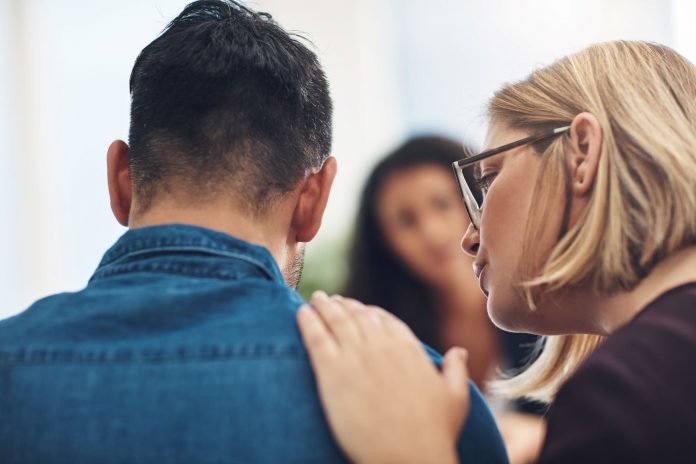
A new Monash University study shows that despite the high rates of mental trauma in adolescents, fewer than half who need to visit a doctor or mental health professional does, instead they are reaching out to medications, family and friends.
The study reveals that young people turn to prescription medication, as well as family and friends for help with their personal and emotional problems because of the barriers they face with accessing mental health care.
Researchers from the Monash Business School, Australian National University (ANU) and The University of Melbourne and published in The Australian Economic Review, found just under half of all children and young people with very high levels of psychological distress accessed any form of mental health care.
Less than two in five children and young people who reported to have self-harmed or attempted suicide accessed any form of mental health care.
Most concerning, of those in high need who accessed mental health care, around one in 10 solely used pharmacological treatments without accompanying mental health services provided by GPs or psychologists.
The study also uncovered an increasing trend in adolescents and young adults accessing prescription medication at younger ages, which may indicate either higher demand or greater access.
Rates of scripts filled among women rise substantially between the ages of 15 and 20 but steadies thereafter, while such rates for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples continue to increase well into their 20s.
A team from Monash Business School’s Centre for Health Economics, including Karinna Saxby, Dr Clement Wong, Dr Sonja de New and Associate Professor Dennis Petrie, along with co-authors Professor Peter Butterworth (ANU) and Dr Chris Schilling (University of Melbourne), looked at how young Australians currently use mental health care and interact with the health care system.
Drawing upon Australian longitudinal administrative and survey data, the team examined the proportion of people who accessed nervous system scripts (which include antidepressants) between the ages of 10 and 30, and its connection to mental health trauma.
Although the proportion of individuals that seek help from medical professionals is higher among those at greater risk of poor mental health, professional help is not the most common source.
Evidence from survey data show that just 14 per cent sought help for personal or emotional problems from doctors, mental health professionals, and phone help lines. In stark comparison, well over 60 per cent of the surveyed adolescents had reached out to friends or family.
“These low rates of professional help seeking may reflect the importance of certain qualities of care and support. Support from parents, friends and other family members is often easily accessible, relies on pre‐existing trust and relationships, and is more likely to be informal, when compared to the process of seeking out help from mental health professionals or the healthcare system in general,” says Dr de New.
“Despite the formal capabilities of mental health professionals or the known benefits of certain medications in treating mental health conditions, informal social support networks through friends and family are likely a major and important source of assistance for many young Australians struggling through the pandemic.”
Dr Wong says navigating Australia’s complex mental health care system contributed to frustration in youth and adults, and substantial treatment gaps with many, if not the majority, of those with mental ill-health not seeking or receiving appropriate treatment.
“Beyond financial factors, social and cultural factors may also influence the use of mental health care. In particular, stigma and negative perceptions surrounding mental illness and preferences for self-reliance may deter young adults from seeking help,” he says.
According to Dr Wong, this youth mental health crisis could be due to cultural changes, such as the increasing role of technology and prevalent use of social media in influencing the mental health and wellbeing of young people.
“Various studies have also considered whether screen time and social media affect health through impaired sleep, reduced physical activity, experiences of cyber-bullying, or even the burden of multi-tasking. But there is not yet any consensus as to whether these contribute to poor mental health,” says Dr Wong.
The Productivity Commission has estimated annual costs of mental illness to the Australian economy to be up to $70 billion. The costs of disability, and premature death due to mental ill-health, suicide and self-harm are believed to be an additional $151 billion.
Self-harm and suicide is the leading cause of death among Australians aged between 15-44 years, with rates of mental disorder at their highest among adolescents and young adults.
Ms Saxby says a lack of help‐seeking in younger populations is consistent with previous work, and was a key factor behind the rollout of Australia’s headspace centres starting in 2006.
“These centres were specifically designed to improve mental healthcare access for young people by providing a youth‐friendly and non-stigmatising environment in which to get mental health care,” says Ms Saxby.
“Given we see that young people still prefer to speak to friends and family regarding their mental health, it suggests that more resources might be required for this population.
“What those resources are, whether providing more education into how to access these services to young people or their parents, or enabling more telehealth for this group, is also important for future research.”